Ever wondered what is OEM unlock and why your Android device would need to have the option enabled? Here’s a complete breakdown of what OEM unlocking your device means, why you’d need it, and how you can do it on any Android phone or tablet in minutes.
Considering the gigantic market share that Android OS enjoys today in the mobile world, it is hard to imagine that it was initially intended to be nothing more than a software platform for digital cameras. More than a decade and millions of dollars’ worth of funds, specialization, and research by Google has led to the Android OS as we know it today. The mobile OS environment has transcended the possibilities of what one could imagine from a portable communication device.
Android OS is among the most effectively open-source software platforms out there, especially compared to the tight-gripped iOS. However, there are elements of Android that are limited by either Google itself, or by the Android OEM brands to which Google provides the software to. Ever since Android OS has been mainstream, so has been the activity of rooting, which essentially allows users to take complete control of their Android devices. While OEM unlock may be a prerequisite of rooting, it tends to offer an entirely different function of its own.
What is OEM Unlock on Android?
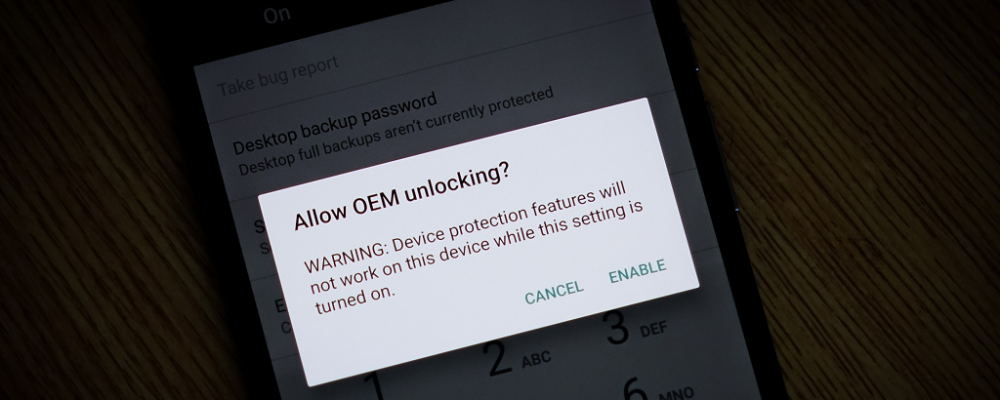
Generally speaking, OEM unlock is a feature that has been included in the Developer Options menu of the Android OS. The feature has been added to the Settings which needs to be enabled before users can choose to unlock the bootloader of their Android device. The bootloader of your Android, once unlocked, unleashes the capability of the device to be rooted, in case it has been restricted to simply one network carrier when it was initially purchased.

The simple function of the OEM Unlock tab in the Developer Options menu is to allow running of the command “fastboot flashing unlock”. The option is hidden from plain sight, since neither Google nor the Android OEM brand of your device wants you to go around tweaking the system beyond what it is intended to do.
Why enable OEM unlock?
Being fair to Google, there aren’t too many features that the company tries to hide from you, and since it has been tucked away OEM unlock away, you must realize that there’s a reason behind it. The primary function of a locked bootloader is to verify the signature of the software every time the mobile device boots up. By removing the bootloader lock, you are essentially allowing the initial security check to be skipped past, which opens doors to techniques such as rooting and installation of custom firmware.
Whether you wish to take complete control of your Android device by rooting it or wish to install a newer, customer firmware on an older device, unlocking the bootloader is the initial step where it all begins. Whether you want to simply achieve superuser access, wish to flash a custom ROM on your device, want to modify the kernel, or install modules to enhance your experience, it all begins with unlocking the bootloader. Even installing a custom recovery such as TWRP requires you to unlock the bootloader of the device first, all of which starts with the OEM unlock option in the Developer Options menu.
Bootloader unlock Vs SIM unlock
Even if you are an avid Android user, chances are that you’ve probably never heard of, or had to find out about terms such as SIM unlock or bootloader unlock. In reality, only a fraction of users will ever feel the need to enhance their user experience with rooting. This is because of the fact that traditionally, rooting was used to enhance the UX, but since new smartphones come with high-end processors that don’t seem to slow down, the mainstream user doesn’t need the feature anymore.

Breaking it down – unlocking the bootloader is what you need to do when you wish to root your Android device or run a custom ROM on it. However, this has nothing to do with the cellular or networking capabilities of your device. If you have a carrier-locked device, learning what is OEM unlock is not going to help you switch out SIM cards and start using other network carriers. To do so, you will need to have your device SIM unlocked either through the network operator or through a reliable third-party SIM unlocking service.
Additionally, rooting can sometimes come with unwanted consequences, such as the inability to use financial apps on a rooted device, which can certainly be a deal-breaker for some. The percentage of users who would wish to unlock the complete networking capabilities of their Android phone are far more likely to look into SIM unlocking services such as Updato, which offers a complete unlocking solution for almost every Android device currently on the market, and supports hundreds of network carriers all across the world.
How to enable OEM unlock
As mentioned earlier, the OEM unlock option is hidden in the Developer Options menu screen, which itself isn’t made visible by default. Hence, you will first need to enable the Developer Options screen and then find the OEM unlock option to turn it on.
Step 1 – Enable Developer Options
To get past the thin veil put in front of the Developer Options before you can access it, here’s what you need to do:
- From the home screen of your Android device, head over to the Settings
- Scroll all the way down to find the System tab and open it.
- Find the About phone tab and select it.
- Scroll down to find the Build number section and tap on it 7 times until you see the message “Congratulations! You’re now a developer”.
Once you’ve completed this process, the new Developer Options menu should appear in the Settings app of your Android device.
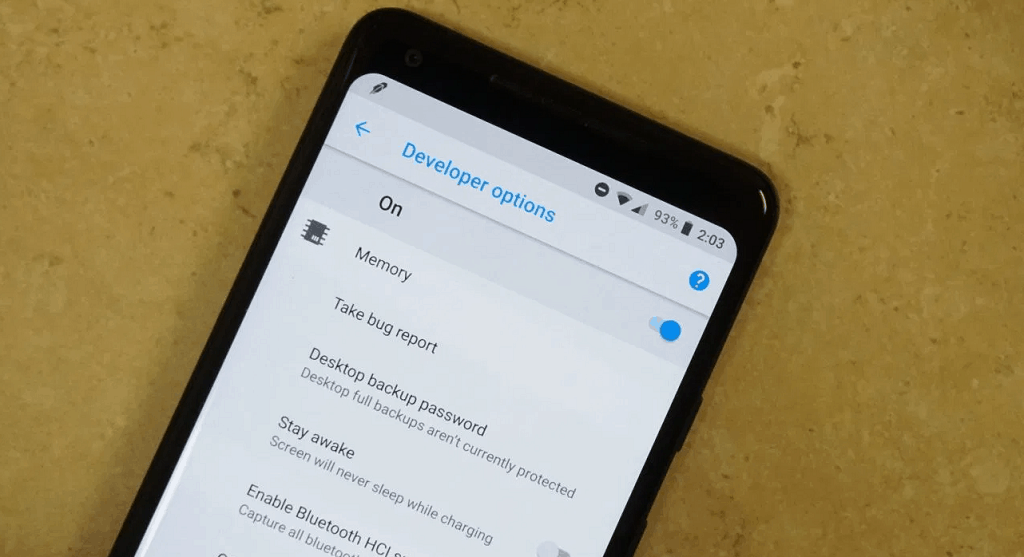
Step 2 – Enable OEM unlocking
- Go back to the Settings app on your Android device.
- Scroll down to find the System
- Now go ahead and look for the OEM Unlock option and press the toggle switch next to it.
Once the switch is enabled, you will be able to unlock the bootloader of your Android device the easy way.
 SamFw
SamFw

